There is a convention in the video, film and television industries which assigns names and guidelines to common types of shots, framing and picture composition. The list below briefly describes the most common shot types.
Notes:

EWS (Extreme Wide Shot)
The view is so far from the subject that he isn't even visible. Often used as an establishing shot.
VWS (Very Wide Shot)
The subject is visible (barely), but the emphasis is still on placing him in his environment.
WS (Wide Shot)
The subject takes up the full frame, or at least as much as comfortably possible.
AKA: long shot, full shot.
MS (Mid Shot)
Shows some part of the subject in more detail while still giving an impression of the whole subject.
MCU (Medium Close Up)
Half way between a MS and a CU.
CU (Close Up)
A certain feature or part of the subject takes up the whole frame.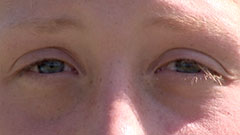
ECU (Extreme Close Up)
The ECU gets right in and shows extreme detail.
Variation: Choker
Cut-In
Shows some (other) part of the subject in detail.
CA (Cutaway)
A shot of something other than the subject.
Two-Shot
A shot of two people, framed similarly to a mid shot.
(OSS) Over-the-Shoulder Shot
Looking from behind a person at the subject.
Noddy Shot
Usually refers to a shot of the interviewer listening and reacting to the subject.
Point-of-View Shot (POV)
Shows a view from the subject's perspective.
Weather Shot
The subject is the weather. Can be used for other purposes, e.g. background for graphics.
Notes:
- The exact terminology varies between production environments but the basic principles are the same.
- Shots are usually described in relation to a particular subject. In most of the examples below, the subject is the boy.
- See below for more information and related tutorials.

EWS (Extreme Wide Shot)
The view is so far from the subject that he isn't even visible. Often used as an establishing shot.

VWS (Very Wide Shot)
The subject is visible (barely), but the emphasis is still on placing him in his environment.

WS (Wide Shot)
The subject takes up the full frame, or at least as much as comfortably possible.
AKA: long shot, full shot.

MS (Mid Shot)
Shows some part of the subject in more detail while still giving an impression of the whole subject.

MCU (Medium Close Up)
Half way between a MS and a CU.

CU (Close Up)
A certain feature or part of the subject takes up the whole frame.

ECU (Extreme Close Up)
The ECU gets right in and shows extreme detail.
Variation: Choker

Cut-In
Shows some (other) part of the subject in detail.

CA (Cutaway)
A shot of something other than the subject.

Two-Shot
A shot of two people, framed similarly to a mid shot.

(OSS) Over-the-Shoulder Shot
Looking from behind a person at the subject.

Noddy Shot
Usually refers to a shot of the interviewer listening and reacting to the subject.

Point-of-View Shot (POV)
Shows a view from the subject's perspective.

Weather Shot
The subject is the weather. Can be used for other purposes, e.g. background for graphics.

No comments:
Post a Comment